Idiopathic Juxtafoveal Telangiectasis (pronounced tell an gee ACT te sis) (JFT), also known as perifoveal telangiectasis or mac-tel for macular telangiectasia, is a condition in which abnormalities develop in blood vessels at the center of the retina. This central part of the retina, called the fovea, is responsible for the sharp vision needed for reading and recognizing faces (see retina diagram).
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Patients with JFT may experience:
- Blurred vision
- Metamorphopsia (pronounced met a morf OP see ah)—a visual disturbance where straight lines appear wavy; parts of the central vision may also appear blank.
- Difficulty reading
- Visual field defects in one or both eyes The condition may be diagnosed before it causes any symptoms at all.
Causes
There are several classifications of idiopathic (of an unknown cause) juxtafoveal telangiectasis (JFT), but the most common one divides JFT into Types 1, 2 and 3. Types 1 and 3 are rare—the vast majority of patients with JFT have Type 2.
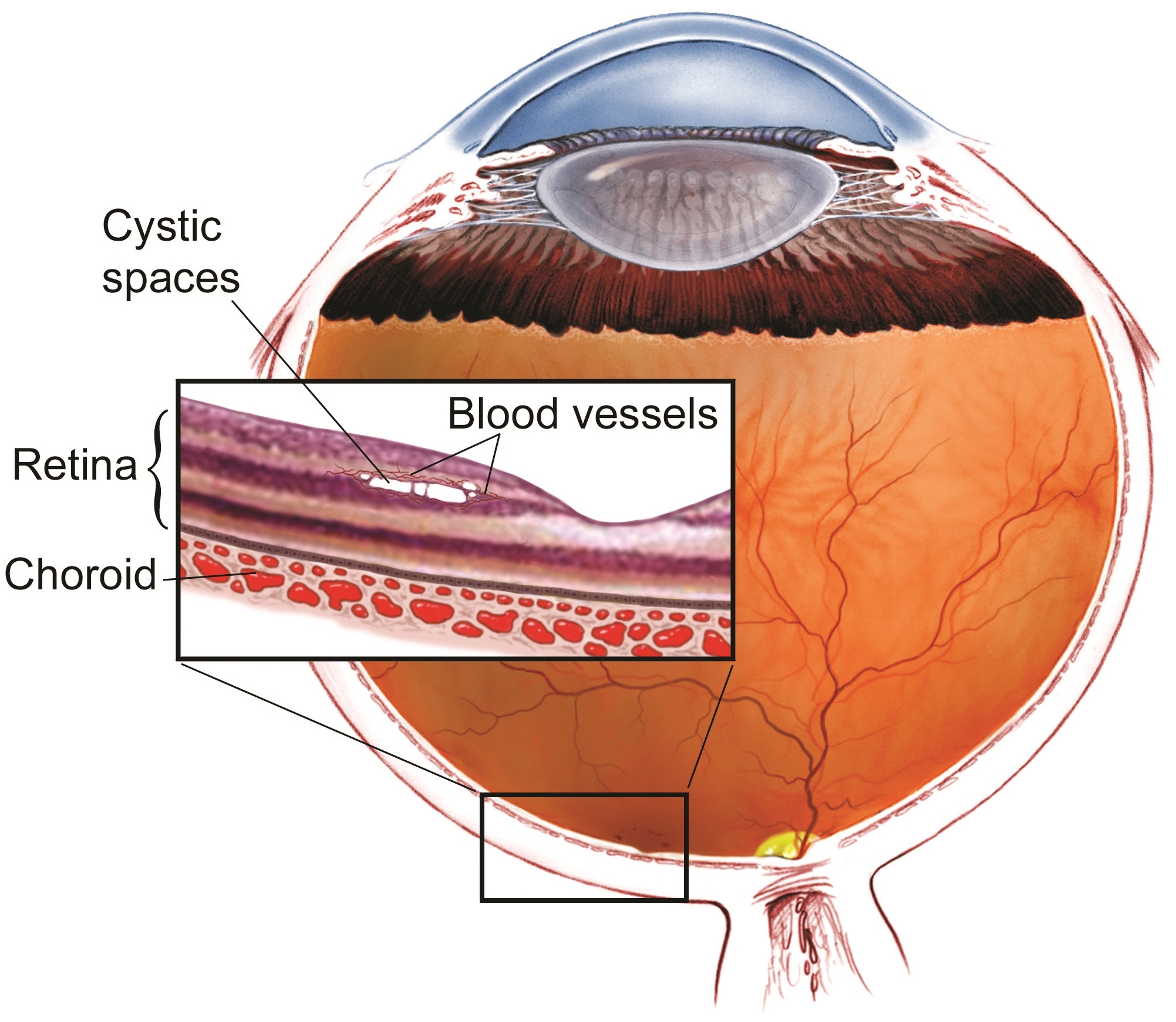
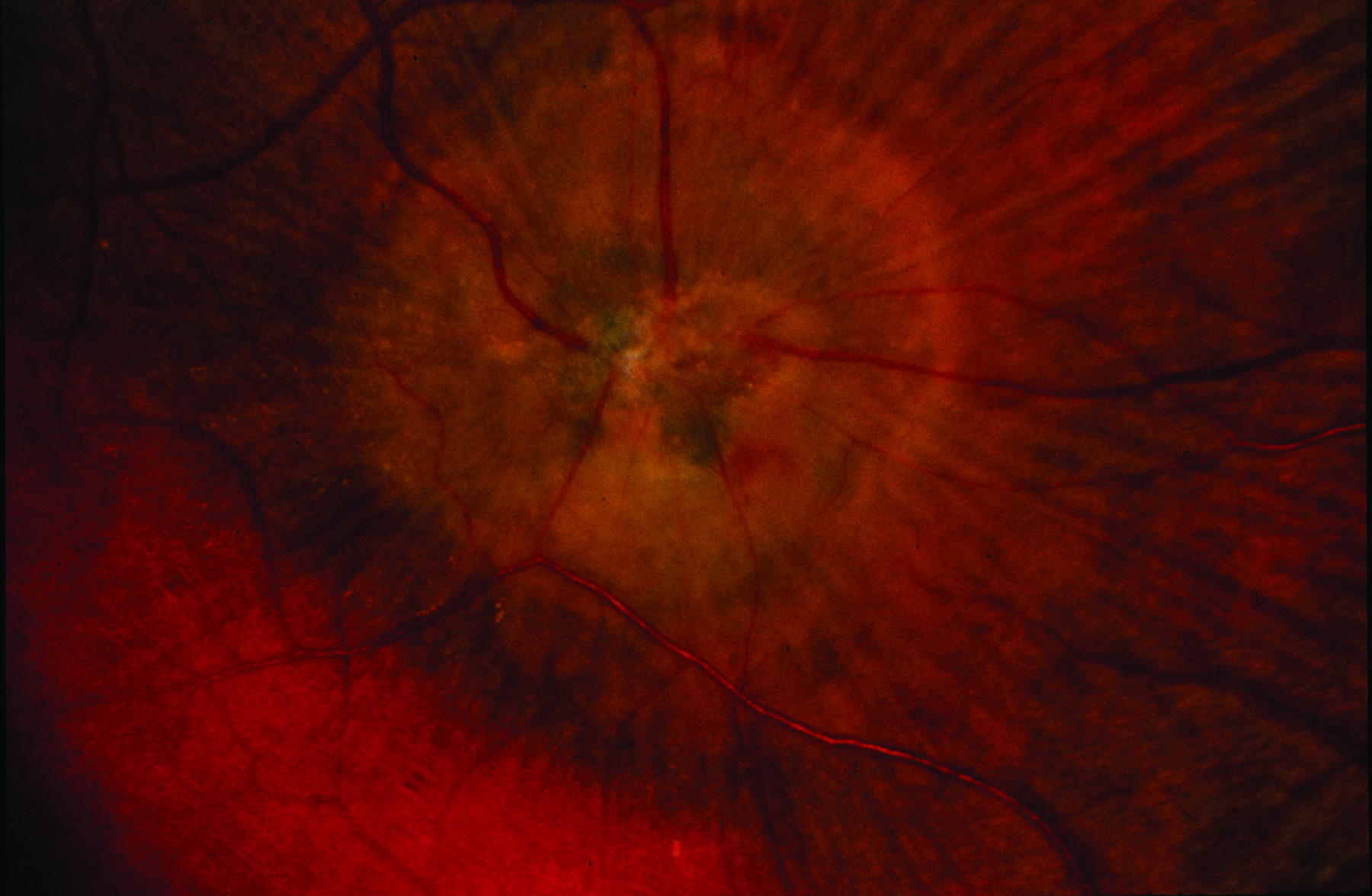
JFT occurs when tiny abnormal blood vessels (or telangiectasias—pronounced tell an gec TAY shuhs) occur in the fovea. Telangiectasias are blood vessels that branch abnormally and may leak fluid or blood into the retina, which is the portion of the eye that house photoreceptor cells that detect light. (Figure 1).
Strangely, many patients with JFT do not have detectable telangiectasias in their retina, only evidence of the retinal damage caused by these abnormal blood vessels.
Although we don’t know what causes JFT Type 2, we do know that it:
- Occurs in men and women at roughly equal rates
- Tends to involve both eyes
- Is more common after age 40
- Is more frequently seen with Type 2 diabetes mellitus or pre-diabetes
Diagnostic Testing
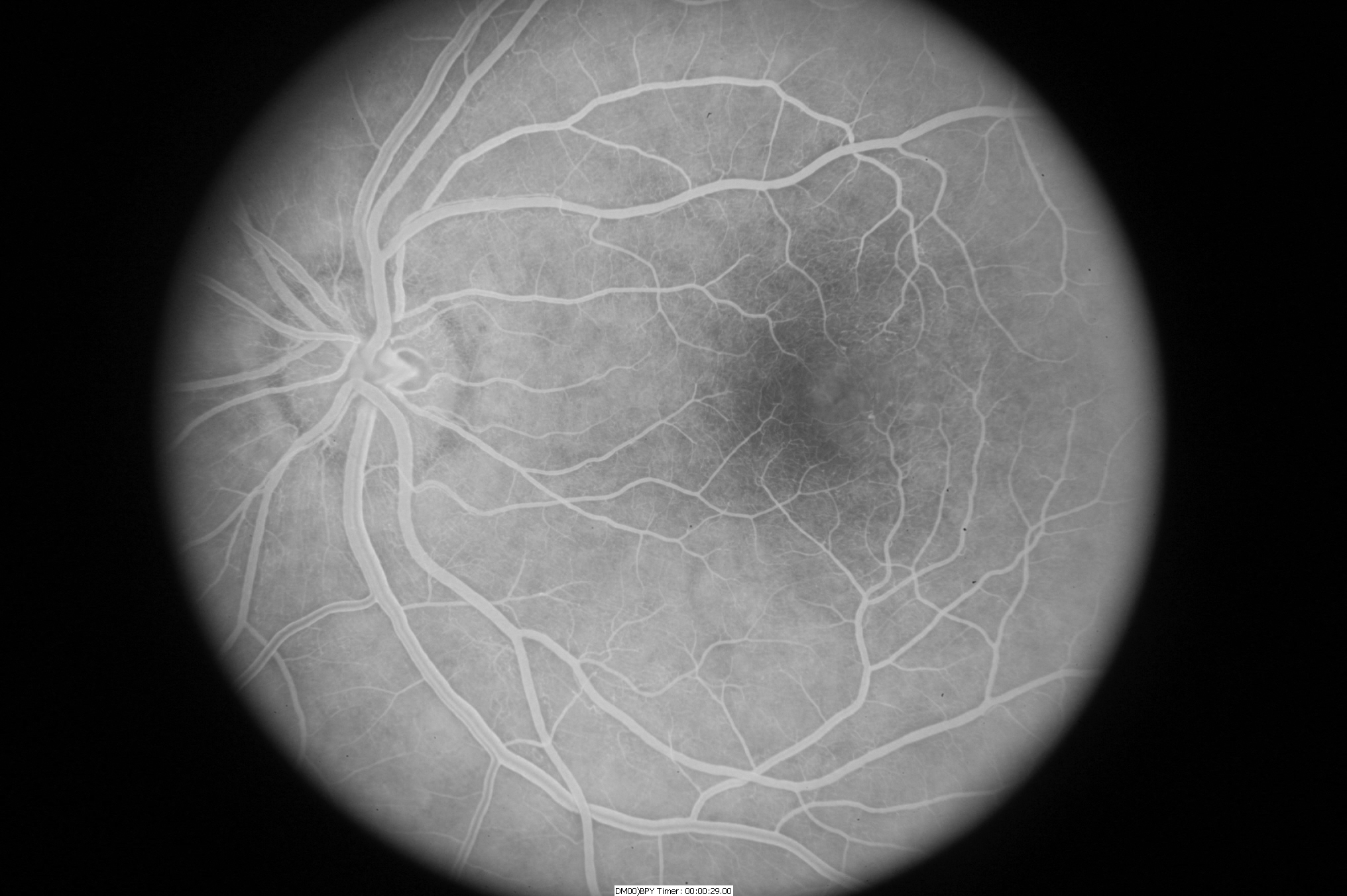
The most important test to diagnose JFT is a careful dilated retinal examination by your retina specialist—certain features such as small bleeds, retinal scarring, or abnormal blood vessels may be detected (Figure 2).
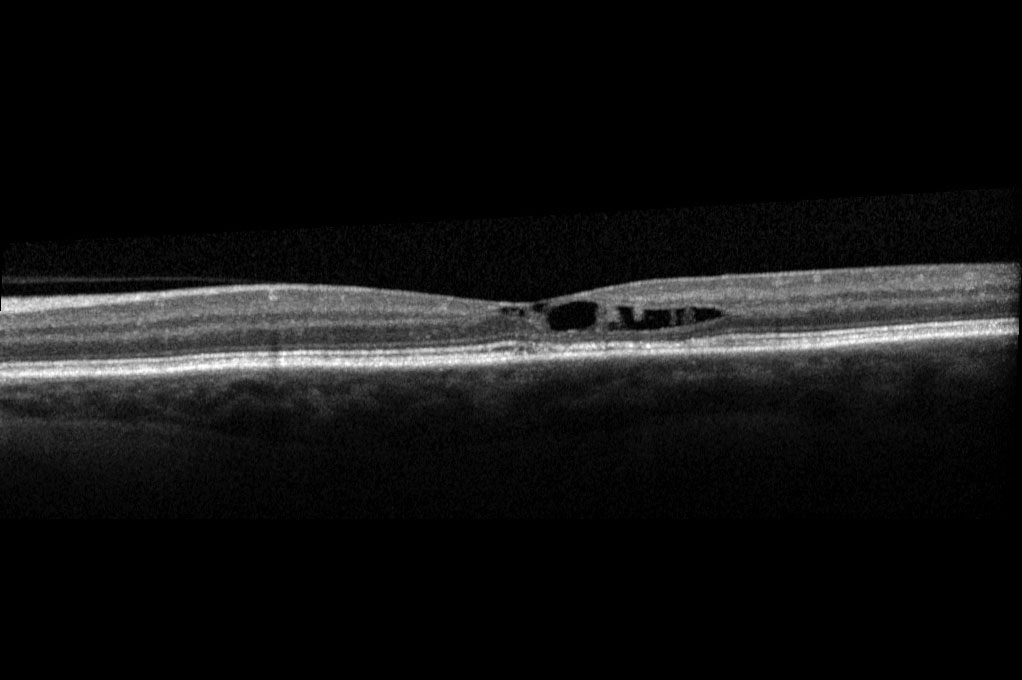
Your retina specialist also may use optical coherence tomography (OCT) to scan the retina, which may show the retinal changes commonly seen with JFT—including abnormal fluid in or under the retina (Figure 3).
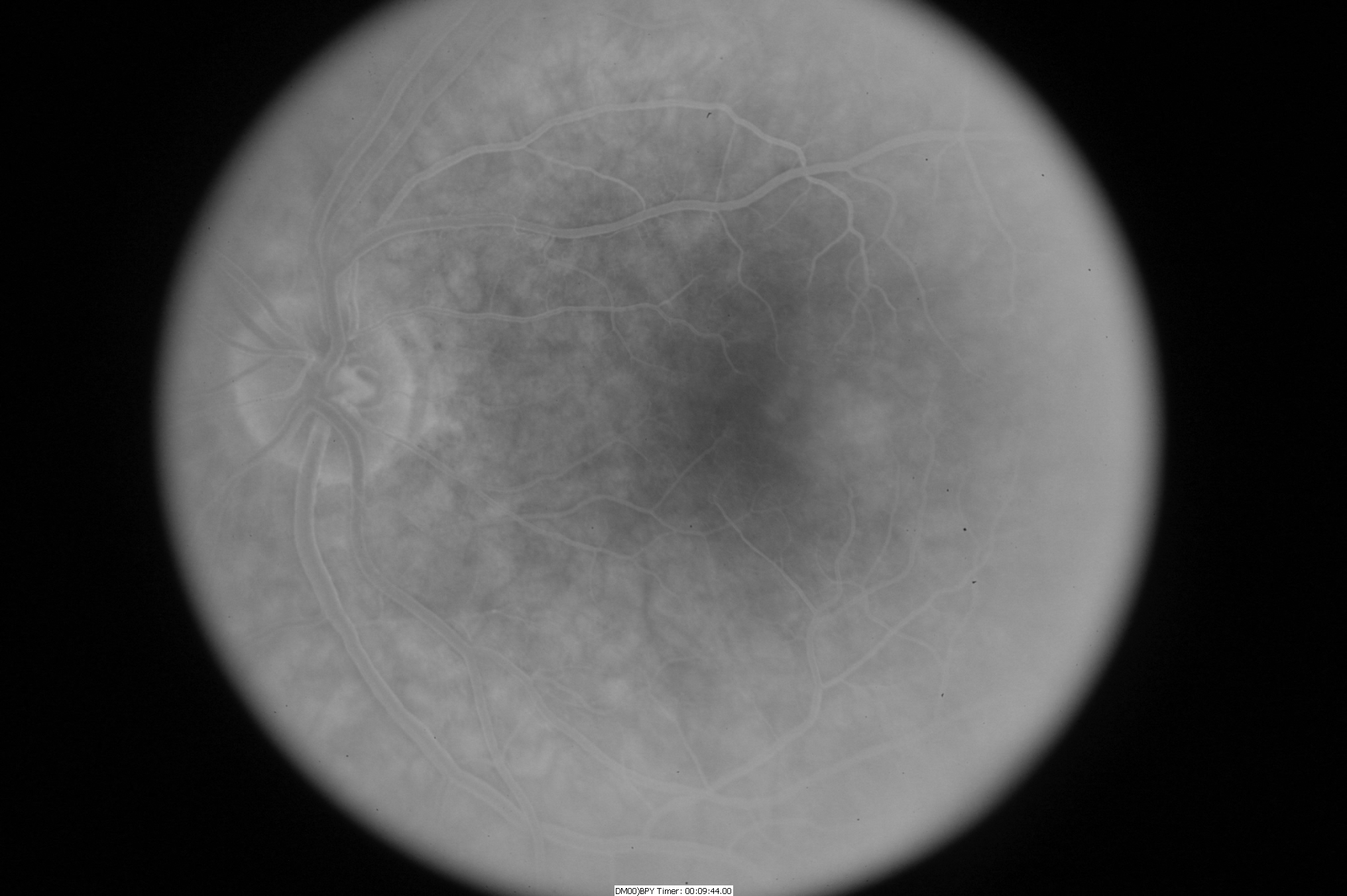
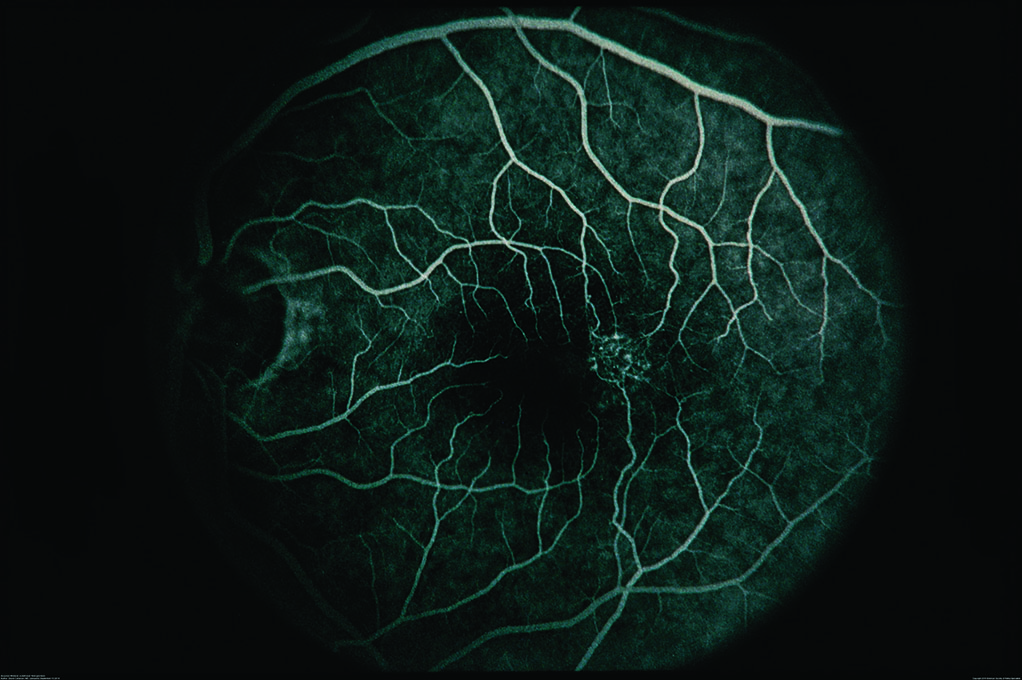
In addition, fluorescein angiography can be important to reveal abnormal and/or leaky vessels in the retina—this test requires an injection of a dye into the vein (usually in the arm or hand) before retinal photos are taken as the dye circulates through the blood vessels (Figure 4).
Treatment and Prognosis
JFT usually results in vision loss when the abnormal blood vessels leak fluid or bleed into or under the retina. JFT may also result in damage to the cells of the retina in the absence of fluid or blood (sometimes called “atrophy”).
Unfortunately, some of the vision loss associated with JFT may be permanent. However, treatments are sometimes useful when fluid or blood are present in JFT—such treatments include injection of anti-VEGF medications into the vitreous gel of the eye or focal/grid laser treatment to the retina.
Although JFT tends to worsen slowly over time, most patients with JFT fortunately maintain useful vision in one or both eyes.
Authors
Thank You To The Retina Health Series Authors
Sophie J. Bakri, MD
Audina Berrocal, MD
Antonio Capone, Jr., MD
Netan Choudhry, MD, FRCS-C
Thomas Ciulla, MD, MBA
Pravin U. Dugel, MD
Geoffrey G. Emerson, MD, PhD
Roger A. Goldberg, MD, MBA
Darin R. Goldman, MD
Dilraj S. Grewal, MD
Larry Halperin, MD
Vincent S. Hau, MD, PhD
Suber S. Huang, MD, MBA
Mark S. Humayun, MD, PhD
Peter K. Kaiser, MD
M. Ali Khan, MD
Anat Loewenstein, MD
Mathew J. MacCumber, MD, PhD
Maya Maloney, MD
Hossein Nazari, MD
Oded Ohana, MD, MBA
George Parlitsis, MD
Jonathan L. Prenner, MD
Gilad Rabina, MD
Carl D. Regillo, MD, FACS
Andrew P. Schachat, MD
Michael Seider, MD
Eduardo Uchiyama, MD
Allen Z. Verne, MD
Yoshihiro Yonekawa, MD
Editor
John T. Thompson, MD
Medical Illustrator
Tim Hengst
Downloads
Copyright 2016 The Foundation of the American Society of Retina Specialists. All rights reserved.